World breastfeeding week, what are the benefits of breastfeeding?

- | آتاماد |
- Viewer: 331
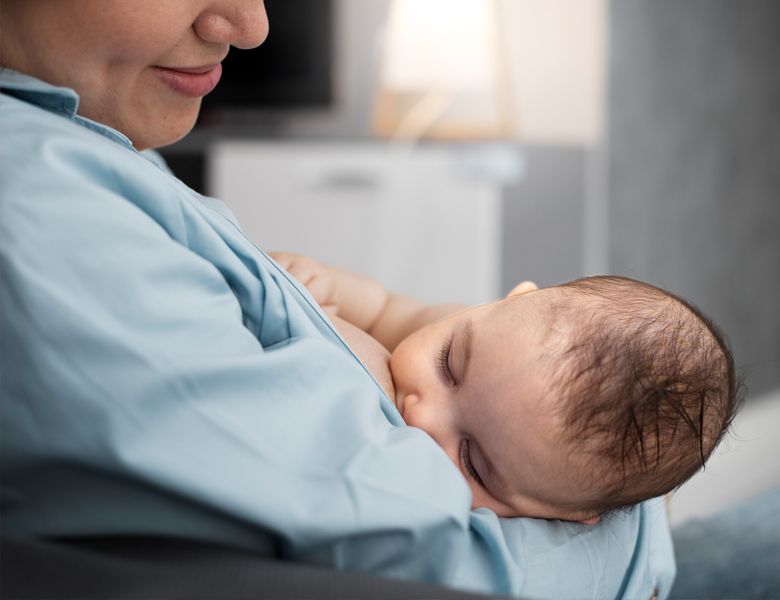
Breastfeeding has many benefits for both the baby and the mother, that are not only limited to nutritional benefits.
Components of breast milk
Breast milk includes many components that meet the baby's needs. Breast milk ensures the baby, helps strengthen the baby's immune system, and contains the right amount of fat, sugar, water, protein, and vitamins needed for the baby's growth.
Benefits of breastfeeding for baby
Research shows that breastfeeding reduces the risk of certain diseases in children by helping to develop a strong immune system. Babies who are breastfed are less at risk of diarrhea, vomiting, preterm necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), respiratory infections, ear infections, bacterial meningitis, asthma and eczema, sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), childhood obesity, type 2 diabetes, leukemia, dental cavities, celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Breast milk provides valuable nutrients for the child until the age of two and guarantees his safety. At least 3 months of breastfeeding reduces the risk of stomach flu, diarrhea, ear infections, and asthma in the first year, breastfeeding for at least 4 months reduces the risk of lower respiratory tract infections, and breastfeeding for at least 6 months reduces the risk of cancer in children.
Dairy foods, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, as well as iodized salt, eggs, and seafood, are important sources of iodine. Higher risks for miscarriage, and perinatal and infant mortality is linked to severe iodine deficiency.
The benefits of breastfeeding for the mother
In the early months after childbirth, breastfeeding reduces the risk of postpartum depression, cancers, osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. In addition to long-term health benefits, breastfeeding results in improving the relationship between the baby and the mother, faster recovery from childbirth, increasing the physical and emotional bond between mother and child, creating mutual trust, it is convenience, and it is easier to reduce the weight gained during pregnancy.
Dairy Foods for Infant Brain Development & Cognition
From conception to the second birthday is a critical period for setting a foundation of brain development that could impact the quality of their life, which depends on the diet before and during pregnancy. Scientists have studied how brain development supports cognition and how nutrition affects both. Nutrition is central to brain development across the lifespan and contributes to it during the first 1,000 days due to the extraordinary rate of human growth, making nutrition a critical factor.
In addition to brain health, dairy has many benefits for children. It is recommended to consume 2 servings of dairy products for ages 2-3 and 2.5 servings for ages 4-8. Research shows that what children drink from birth to age 5 significantly affects their health, with milk and water being the best choices. Calcium, protein, selenium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and vitamins A, B12, and D in dairy products help strengthen the immune system, build healthy bones, and support healthy weight in children. In addition, by providing about 8% of the daily value of choline, milk helps the development of the child's brain, especially in the first 3 years of life.
When Can Babies Have Milk and Dairy Foods?
Infancy and early childhood is a key time to learn to establish dietary habits. But how much milk, or dairy products can they have, and starting at what age?
• 0-6 months
: Exclusive breastfeeding is recommended for at least the first 6 months followed by breastfeeding along with a variety of nutrient-dense complementary foods from all food groups, including dairy foods to support early growth.
Food allergies, including dairy milk allergies, are rare and typically develop in the first two years after birth, then decline through childhood. It is recommended to introduce potentially allergenic foods, including dairy foods, after the first six months.
• 6-12 months:
Introduce foods like whole milk yogurt and cheese, eggs, iron-fortified cereal, and fruits and vegetables to help baby learn to like a variety of healthy foods. An early introduction to some potentially allergenic foods may help reduce the risk of developing a food allergy. And while cow’s milk itself should not be introduced until the baby turns one year of age, cheeses and yogurt can be introduced starting at 6 months.
• 12 months:
As part of a healthy diet for 1- to 2-year-olds, it is recommended to consume 1 2/3- to 2-cup equivalents of dairy foods (whole milk , yogurt, cheese) depending on daily calorie needs.
• 2-5 years:
Switch from whole milk to low-fat or fat-free dairy milk. Aim for 2 to 2 1/2 cups a day of milk, cheese, and/or yogurt.
For toddlers with confirmed dairy milk allergy and lactose intolerance , the only acceptable plant-based alternative to dairy milk is unsweetened fortified soy beverage. Other plant-based beverages lack or fall short of key nutrients found in dairy milk.
Plant alternatives are not recommended for toddlers and children
Among the many plant-based milk alternatives available, fortified soy-based beverage is the only acceptable alternative for approximately 4% of children with dairy milk allergies. Although often labeled as "milk", many plant-based milk alternatives lack the nutrients found in dairy milk. Researchers state that consumption of plant-based milk without compensating nutrients that plant alternatives lack, causes insufficient growth, malnutrition, and metabolic and electrolyte disorders in children. In addition, most of which contain lower protein content and protein quality than dairy milk.
What does affect the duration and intention of breastfeeding
Studies showed that the initiation and duration of breastfeeding depend on a combination of biological, psychological, and Socio-demographic factors.
1. Socio-demographic factors
Studies have shown that there are significant differences between the age of women and the breastfeeding process. we thought that younger women were just as likely to initiate breastfeeding as older women but we found out that they had almost twice the odds of not being willing to breastfeed their baby Compared with older mothers. Also, the results indicated that young mothers were less willing to breastfeed.
The early end of the breastfeeding process is related to the full-time employment of the mother. Women with part-time jobs are more likely to continue breastfeeding their babies than full-time working mothers. Mothers who returned to work early were more likely to end breastfeeding.
2. Psychological factors
Examining shows that mothers' feelings about their ability can affect the duration of breastfeeding. In general, this feeling of mothers in the first three days after giving birth is strongly related to the breastfeeding period. Other important psychological factors that affect the duration and intention of breastfeeding include the mother's psychological approach during pregnancy and psychological adaptation during the breastfeeding process.
It is interesting to know that women who were breastfed during infancy were more likely to breastfeed their children than mothers who were formula fed. Results obtained from a study of mothers who recently gave birth showed that women who did not receive nutrition counseling or support from their spouse, or parents were more likely to stop breastfeeding.
Moreover, emotional stability, extroversion, and conscientiousness have been proven to be inversely related to breastfeeding cessation.
3. Biological factors
Smoking during breastfeeding is associated with an increased rate of premature end of breastfeeding. In fact, nicotine poses a negative effect on the volume of breast milk produced and the sleep patterns of infants. Only 23% of mothers who smoke breastfed their children for six months after giving birth. Overweight mothers are less likely to initiate breastfeeding in the postpartum period. It is suggested that women who were overweight before pregnancy should shorten the period of breastfeeding. More than 50% of mothers who gave birth by cesarean have breastfed their baby only two months after giving birth. Women who experienced postpartum complications breastfed their babies for a shorter period.
References:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15274-benefits-of-breastfeeding
https://www.usdairy.com/news-articles/infant-and-childhood-nutrition-and-cognition
https://www.usdairy.com/news-articles/when-can-babies-have-milk-and-dairy-foods
https://www.usdairy.com/news-articles/cottage-cheese-for-babies
https://www.usdairy.com/news-articles/can-babies-have-yogurt
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9923068/
GET IN TOUCH
Copyright © 2023 Atamad.com All right reserved
Website design and SEO services by Seohama team – Web hosting by Sarverhama
Copyright © 2023 Atamad.com All right reserved
Website design and SEO services by Seohama team – Web hosting by Sarverhama