What are the detrimental effects of consuming adulterated milk on health?

- | آتاماد |
- Viewer: 264
Food adulteration
Food adulteration refers to the act of either adding or replacing food substances with undeclared alternative components or by the removal of some valuable components incidentally or intentionally. Incidental or unknown adulteration is found in food due to ignorance, negligence, lack of proper facilities, or packaging hazards like larvae of insects, pesticide residues, etc. In this type, the ways the product is produced, processed, stored, transported, and marketed may be the places where they were contaminated. Intentional adulteration, the most dangerous one, is done due to reasons like the demand and supply gap, increased profit margin, low purchasing capability of customers, reduced production cost, and lack of suitable detection tests. A global health concern, food adulteration can pose serious health risks and even lead to fatal diseases. Also, developing countries are at greater risk due to a lack of monitoring and policies.
Factors affecting milk composition
Milk composition can affect by genetic factors, species of animal, and environmental factors like the interval between milking and the stage of lactation. Fat, protein, and total solids of milk are easily impacted by genetics. This indicates that some genetics of milking cows have high fat and protein composition percentages. As for the environmental factors, the fat content varies considerably between morning and evening milking. The stage of lactation also affects the fat, lactose, and protein contents of milk. SNF content is usually highest during the first 2-3 weeks, after which it decreases slightly. Fat content is high immediately after calving but soon begins to fall for 10 to 12 weeks, then until the end of the lactation it tends to rise again.
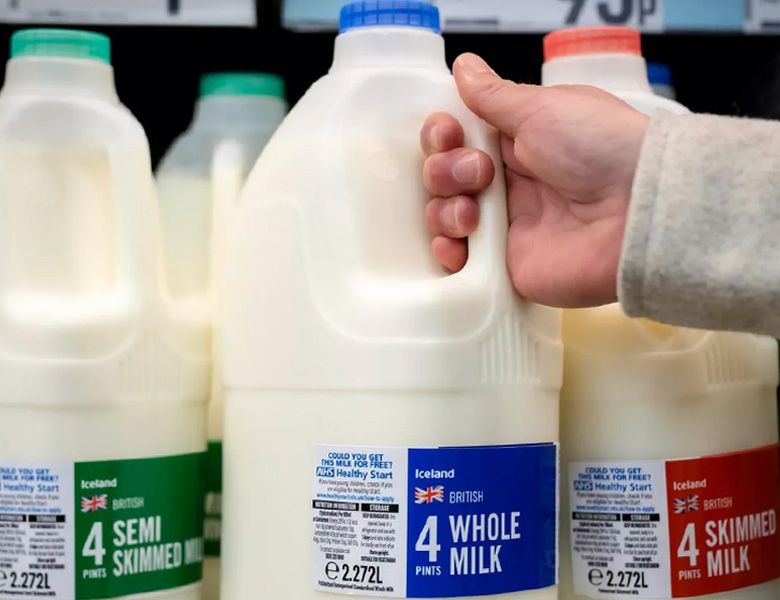
Milk adulteration
Unfortunately, due to the perishable nature of milk, it is easily adulterated in different ways, like the addition of neutralizing agents, thickening agents, and preservatives. Water, starch, urea, flour, formalin, cane sugar, and sodium hydroxide are the common adulterants used. We are going through the effects of these adulterants on the quality and safety of milk.
1. Diluted agents:
The most common form of milk adulteration is adding water to increase its volume and higher profit. Neutralizing the developed acidity of milk for prolonged shelf life is yet another reason. Adding water alters the composition and reduces the foamy appearance, specific gravity, and nutritional value of milk. This not only reduces its nutritional value, but if the water was contaminated it can also cause additional health problems and harmful waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid, shigella, polio, meningitis, and hepatitis A and E. Moreover, contaminated water may cause stomach disorders in elders and serious health hazards in infants and children whose basic diet is milk. Adding salt, sugar, and starch are methods of masking added water in milk. The methods of detection include the determination of milk’s specific gravity and freezing point of milk.
2. Thickening agents
The viscosity of milk can be changed by skimming or the addition of water. Thickening agents like wheat flour, rice flour, starch, dextrin, sugar, skim milk powder, and urea are added to the milk to increase solids content, viscosity, and masking water adulteration, with starch being the most common.
Undigested starch in the colon, which is due to the consumption of higher amounts of starch, may lead to diarrhea. Its accumulation in the body may be fatal for diabetic patients.
Added cane sugar in milk plays a role in maintaining the sweet taste of milk which is usually lost by water adulteration. Also, sugar is added to milk in order to raise the specific gravity of the diluted milk.
Urea is added to milk to provide whiteness, increase the consistency and shelf life of milk, and for standardizing the content of solids-not-fat present in natural milk. Urea-containing milk is quite harmful to pregnant women, children, and sick individuals. The presence of urea above the upper limit in milk can cause severe health problems, including indigestion, acidity, ulcers, cancer, malfunctioning of kidneys, and osteoporosis.
3. Neutralizers and salts
Neutralizers are added to milk to decrease the acidity of milk. The acidity is increased due to microbial actions, if the time between milking and consuming passes long, making the milk unsuitable for processing. Neutralizers are generally used to mask the developed acidity or bitter taste in milk. Sodium hydroxide is the most common neutralizer in this group.
Sodium hydroxide can be very harmful if ingested. Its ingestion may result in a burning sensation, abdominal pain, or shock.
Sodium carbonate also referred to as soda ash can cause severe health hazards if ingested, like gastrointestinal problems including gastric ulcers, diarrhea, colon ulcers, and vomiting. High amounts of carbonates and bicarbonates disrupt hormone signals regulating development and reproduction. Levels of carbonates and bicarbonates in milk samples give higher alkalinity, which causes milk-alkali syndrome resulting in systemic alkalosis, renal failure, high blood pressure, cardiac failure, and edema.
To mask the effect of added water and increase the lactometer reading and SNF content of the milk, sodium chloride is added. It has been reported that high levels of sodium chloride in milk could affect the acid-base balance in the body and may develop regression loss of acquired immunity, kidney problems, speech, and sensory disturbances. Salt in adulterated milk can cause serious health problems like heart disease, gastrointestinal disturbance, problems with kidneys, raised blood pressure, and allergies. However, higher levels of salts sometimes might be due to late lactation milk, subclinical mastitis, and disease conditions which cannot be overcome.
4. Preservatives
To increase the shelf life of liquid milk, preservatives like formalin, hydrogen peroxide, and boric acid are added unscrupulously to milk which may prove hazardous to human health. A positive relationship between daily temperature and intensity of using chemicals as preservatives are normally observed, as high temperature increases the multiplication of microbes and increases the acidity and making the milk unacceptable. Thereby, preservatives are added to inhibit microbial growth and increase the shelf life of milk and avoid
financial losses.
Formalin is a potentially hazardous toxic, and potent carcinogen. Formalin is used to adulterate milk to neutralize milk or increase its shelf life. Consumption of an elevated dose of formalin can cause vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and also blindness.
The main reason for adding hydrogen Peroxide to milk is to prolong its freshness but peroxides damage the gastrointestinal cells which leads to gastritis and inflammation of the intestine. Hydrogen peroxide adulteration disturbs antioxidant activity and natural immunity, which leads to increased aging. It also disrupts the development and reproduction hormones and damages the stomach cells, gastritis and inflammation of the intestine, and bloody diarrhea.
Boric acid also causes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, kidney damage, acute failure of the circulatory system, and even death.
Bottom line
Milk adulteration is becoming a serious problem in the world. About 68% of milk delivered to consumers is not as per standards. Consumption of adulterated milk may lead to serious health issues. Hence it is important to have an efficient and reliable quality control system that will regularly monitor and ensure a quality supply of milk to the consumer.
Reference:
https://www.opastpublishers.com/open-access-articles/effect-of-adulterants-on-quality-and-safety-of-cow-milk-a-review.pdf
Milk Adulteration and Its Impact on Consumer Health: A Review
Popular Articles and News
GET IN TOUCH
Copyright © 2023 Atamad.com All right reserved
Website design and SEO services by Seohama team – Web hosting by Sarverhama
Copyright © 2023 Atamad.com All right reserved
Website design and SEO services by Seohama team – Web hosting by Sarverhama